Python Apis: Part 1
Author: R Zach FeeserA classic approach to teaching code to screen interactions is by using a “turtle”. This approach asks students to use the coding language they are studying to move a basic “turtle” (it’s a dot) around on the X,Y axis of their screen. Python has a “Turtle Graphics Module” that is built on top of Tkinter, which is a more powerful, general purpose Python library for building GUIs (Graphical User Interfaces). Using this library, we will set the background as a world map of the planet Earth, replace the “turtle” with an International Space Station (ISS) icon, and then tell our new ISS-turtle to move according to real-time data provided by a RESTful API that tracks the actual location of the orbiting ISS.
Step 1 - Prerequisites to Perform this task.
- Install latest version of python (python3.X)
- Ubuntu 16.04 or greater.
- Map to show International Space Station
- Internatnional Space Station :)
Step 2 - Install python3 packages tkinter.
student@bchd:~$ sudo apt install python3--tk -y
Step 3 - Make a directory for your code.
student@bchd:~$ mkdir apicode
student@bchd:~$ cd apicode
student@bchd:~/apicode$Step 4 - Create your python script and review!
You can do this with any of your favorite editors like vim, nano, or emacs. Here we just use leafpad.
student@bchd:~/apicode$ leafpad apicode.py
import urllib. request # easily replaced by the requests library
import json # needed to translate JSON attachment because we use urllib.request
## Trace the ISS - earth-orbital space station
eoss = 'http://api.open-notify.org/iss-now.json'
## Call the webserv
trackiss = urllib.request.urlopen(eoss)
## put into file object
ztrack = trackiss.read()
## json 2 python data structure
result = json.loads(ztrack.decode('utf-8'))
## display our pythonic data
print("
Converted python data")
print (result)
input('
ISS data retrieved & converted. Press any key to continue')
location = result['iss_position']
lat = location['latitude']
lon = location['longitude']
print('
Latitude: ', lat) Step 5 - In your browser, check out the url, which is the value for the eoss variable.
Open your browser to a new tab with this URL: http://api.open-notify.org/iss-now.json
{"iss_position": {"latitude": "-27.8149", "longitude": "-112.1983"}, "timestamp": 1609361386, "message": "success"}Step 7 - Run your python code!
student@bchd:~/apicode$ python3 apicode.py
Converted python data
{'iss_position1: {'longitude': '48.1352', 'latitude': '10.0497'}, 'timestamp': 1532355812, 'message': 'success’}
ISS data retrieved & converted. Press any key to continue
Latitude: 10.0.497
Longitude: 48.1352Step 8 - Gather the rest of the Prerequisites.
student@bchd:~/apicode$ wget https://static.alta3.com/images/python/iss_map.gif -O iss_map.gif
student@bchd:~/apicode$ wget https://static.alta3.com/images/python/spriteiss.gif -O spriteiss.gif
Step 9 - Create an updated python script.
student@bchd:~/apicode$ leafpad apicode02.py
import turtle
import urllib.request
import json
## Trace |the ISS - earth-orbital space station
eoss = 'http://api.open-notify.org/iss-now.json'
## Call the webserv
trackiss = urllib.request.urlopen(eoss)
## put into file object
ztrack = trackiss.read()
## json 2 python data structure
result = json.loads(ztrack.decode('utf-8'))
## display our pythonic data
print("
Converted python data")
print(result)
input('
ISS data retrieved & converted. Press the ENTER key to continue')
location = result['iss_position']
lat = location['latitude']
lon = location['longitude']
print('
latitude: ', lat)
print('Longitude: ', lon)
screen = turtle.Screen() # create a screen object
screen.setup(720, 360) # set the resolution
screen.setworldcoordinates(-180,-90,180,90)
screen.bgpic('iss map.gif')
screen.register shape('spriteiss.gif')
iss = turtle.Turtle()
iss.shape('spriteiss.gif')
iss.setheading(90)
lon = round(float(lon))
lat = round(float(lat))
iss.penup()
iss.goto(lon, lat)
turtle.mainloop()| # <-- this line should ALWAYS be at the bottom of your script. It prevents the graphic from closing!!Step 10 - Run your new code!
student@bchd:~/apicode$ python3 apicode02.py
Converted python data
{'message': 'success', 'timestamp': 1532356659, 'iss_position': {'longitude': '93.1921', 'latitude': '46.5445'}}
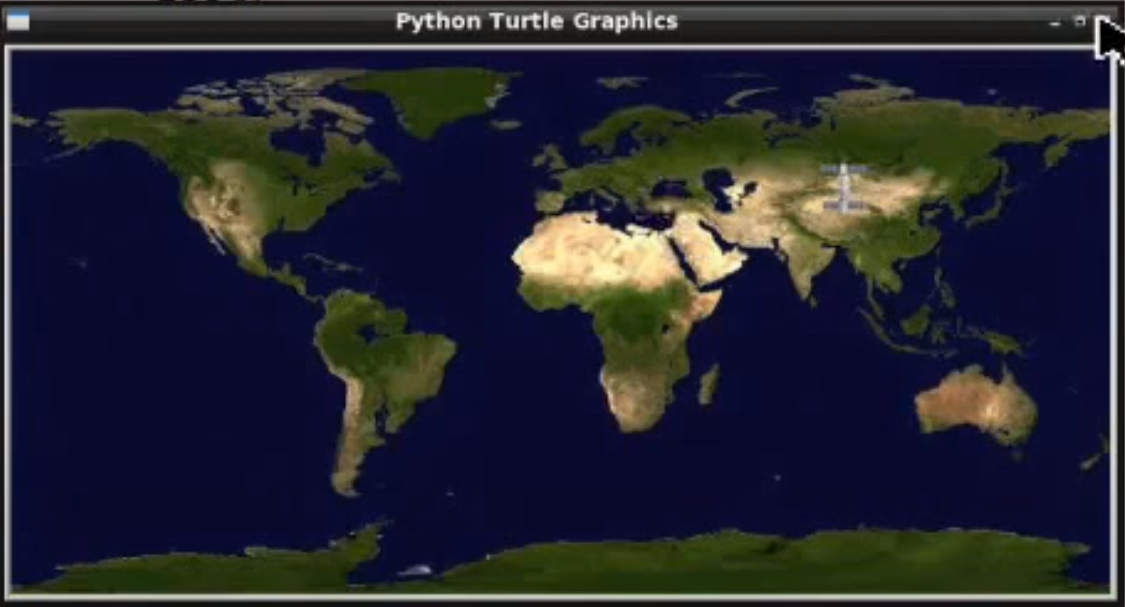
ISS data retrieved & converted. Press the ENTER key to continueStep 11 - Take a look at the Map that shows where the International Space Station is at the moment! Awesome!
If you run that code again, you will see the International Space Station has moved coordinates. It moves with haste.
See PART 2 for more…